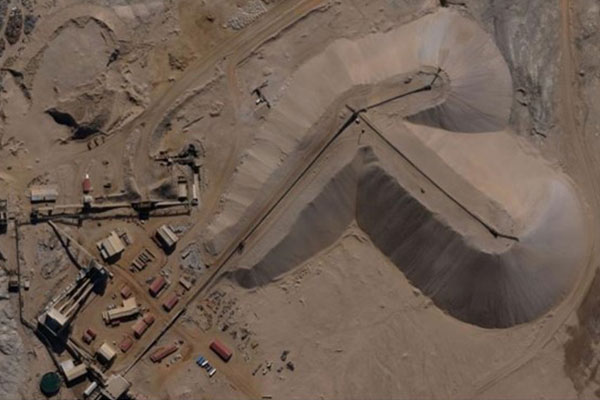
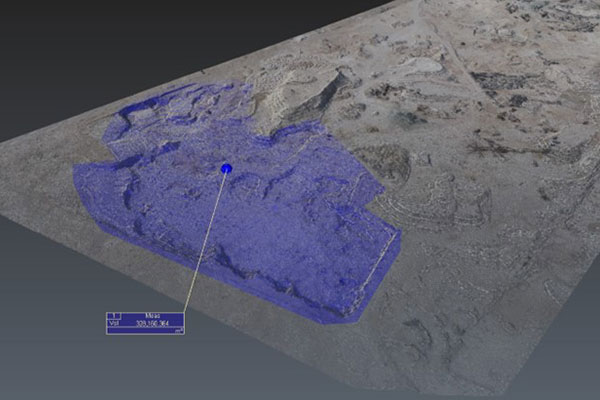
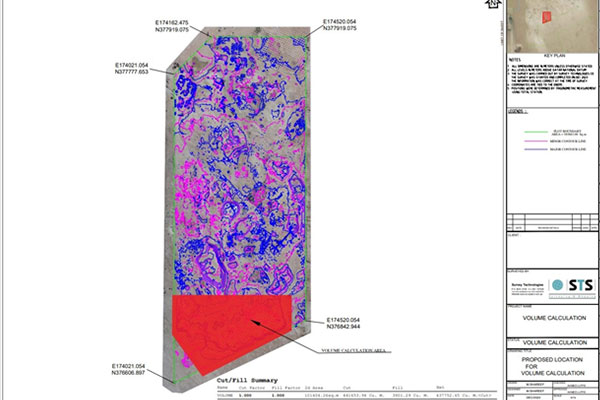
The main goal of volume calculation is to find out the volume of material excavated or stacked in a predefined area and check whether the volume corresponds to the expected value mentioned in the project documentation. The volume is determined by a difference of topographies from two survey phases or by a difference between the survey and the project documentation. It is possible to measure even mounds of fine and loose materials or dangerous, difficult-to-access objects in very accurate way. High measurement speed is an indisputable advantage.
Groundwork
This involves tasks such as excavation and backfilling.
Disposal area management
STS manages areas designated for the disposal of materials.
Material transfer
STS oversees the transfer of materials between different locations.
When it comes to volume calculation, there are various methods available. One of the simplest methods involves utilizing digital terrain/surface models (DTM / DSM). These models are created using data obtained from aerial photography or terrestrial scanning. By employing complex surveys with a substantial number of points, the resulting 3D models are minimally generalized. As a result, the calculated volume more accurately reflects the real state compared to methods utilizing total station or GNSS technology.
There are several methods of volume calculation. The easiest one is based on digital terrain / surface models (DTM / DSM). Data obtained by aerial photography or terrestrial scanning are used to create digital terrain / surface models. Thanks to the complex survey with significant number of points, final 3D models are minimally generalized and therefore calculated volume reflects the real state better than in the case of using total station or GNSS.